1. Introduction to Huffman Coding
Huffman coding is a lossless data compression algorithm that assigns variable-length codes to input
characters, with shorter codes assigned to more frequent characters. This results in an overall reduction in
file size while preserving all original information.
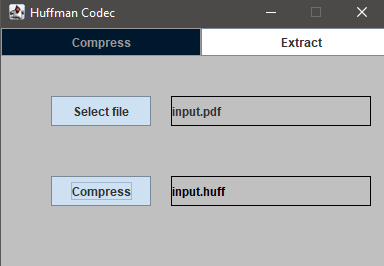
This Java-based application provides a GUI interface to perform Huffman compression and
extraction on any file type. The user can compress any file into a custom .huff format, and
later extract the original content using the embedded metadata and Huffman decoding logic.
2. Key Features of the Application
- Universal File Support: Compresses and extracts any file format by handling binary data
directly.
- Custom File Format: Encoded files use the .huff extension and include headers for accurate
decompression.
- Embedded Metadata: Stores file extension, padding information, and a complete byte frequency table
in the output file.
- Progress Feedback: Uses a JProgressBar to provide visual feedback during long
operations.
- Navigation Panel: Provides a switchable interface between Compress and Extract views
using a clean tab-like design.
3. How Huffman Compression Works
- Frequency Table Creation: Each byte (0–255) is counted using
HuffmanEncoder.buildFrequencyTable() to determine its frequency in the file.
- Huffman Tree Generation: A binary tree is built using a priority queue where nodes with
lower frequency have higher priority. Ties are broken lexicographically.
- Code Generation: A recursive traversal generates a binary code for each byte, stored in a
HashMap<Byte, String>.
- Encoding: The original file is re-encoded using these binary codes and written using
BitOutputStream, which handles individual bit-level writing.
- Header Writing: Metadata such as file extension, frequency table, and padding are prepended using
HuffmanEncoder.writeHuffFile().
4. What is happening
Each byte (0–255) is treated like
a "symbol". We count how many times each byte appears in the file (its frequency).
Each byte
becomes
a leaf node in a binary tree. All leaf nodes go into a priority queue (a special kind of queue
that gives you the smallest thing first).
Nodes with lower frequencies are more important
here—they
get processed first. If two nodes have the same frequency, the one with the lower byte value
(lexicographical order) goes first. This is how ties are broken.
We build the tree from the
bottom
up: Pull out the two smallest nodes, combine them into a new node whose frequency is the sum of both,
put the new node back in the queue. Repeat until only one node is left—this is the root of the
Huffman tree.
We walk the tree: Going left adds a '0' to the code, going
right adds a '1'. Once we reach a leaf node (i.e., a symbol), we record the code string
we built along the way in a map. The final result: a HashMap<Byte, String> where each
byte has its unique binary code.
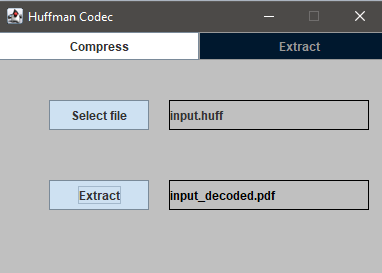
5. How Huffman Extraction Works
- Header Reading: The decoder reads the file extension, padding value, and frequency table using
HuffmanDecoder.readHeader().
- Tree Reconstruction: The same Huffman tree is rebuilt from the frequency table.
- Bit-by-Bit Decoding: Using BitInputStream, each bit from the encoded file is read and
navigated through the Huffman tree until a leaf (byte value) is reached.
- File Output: The decoded bytes are written to a new file with the original extension, restoring the
exact original file.
Compressing a PDF file
Extracting a compressed file
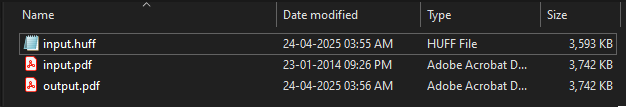
Comparing file sizes before and after compression.
The original and extracted files have the same size,
while the compressed .huff file is smaller
6. Technical Components and Design
- Bit-Level I/O: The BitInputStream and BitOutputStream classes enable precise reading
and writing of individual bits, which is essential for Huffman coding.
- Custom Nodes: The HuffmanNode class represents tree nodes and implements Comparable
to support min-heap ordering.
- Panel Switching: HuffmanCodec acts as the main controller and swaps between
CompressionPanel and ExtractionPanel via the NavBar.
- Threaded Execution: Compression and extraction run in background threads to keep the GUI
responsive, and use SwingUtilities.invokeLater() to update the UI.