1. Introduction
This is a fully functional news and weather portal built using HTML, CSS,
JavaScript, PHP, and Bootstrap. It provides real-time access to top news categories and
weather details in a clean, responsive interface.
2. Key Features and Functionalities
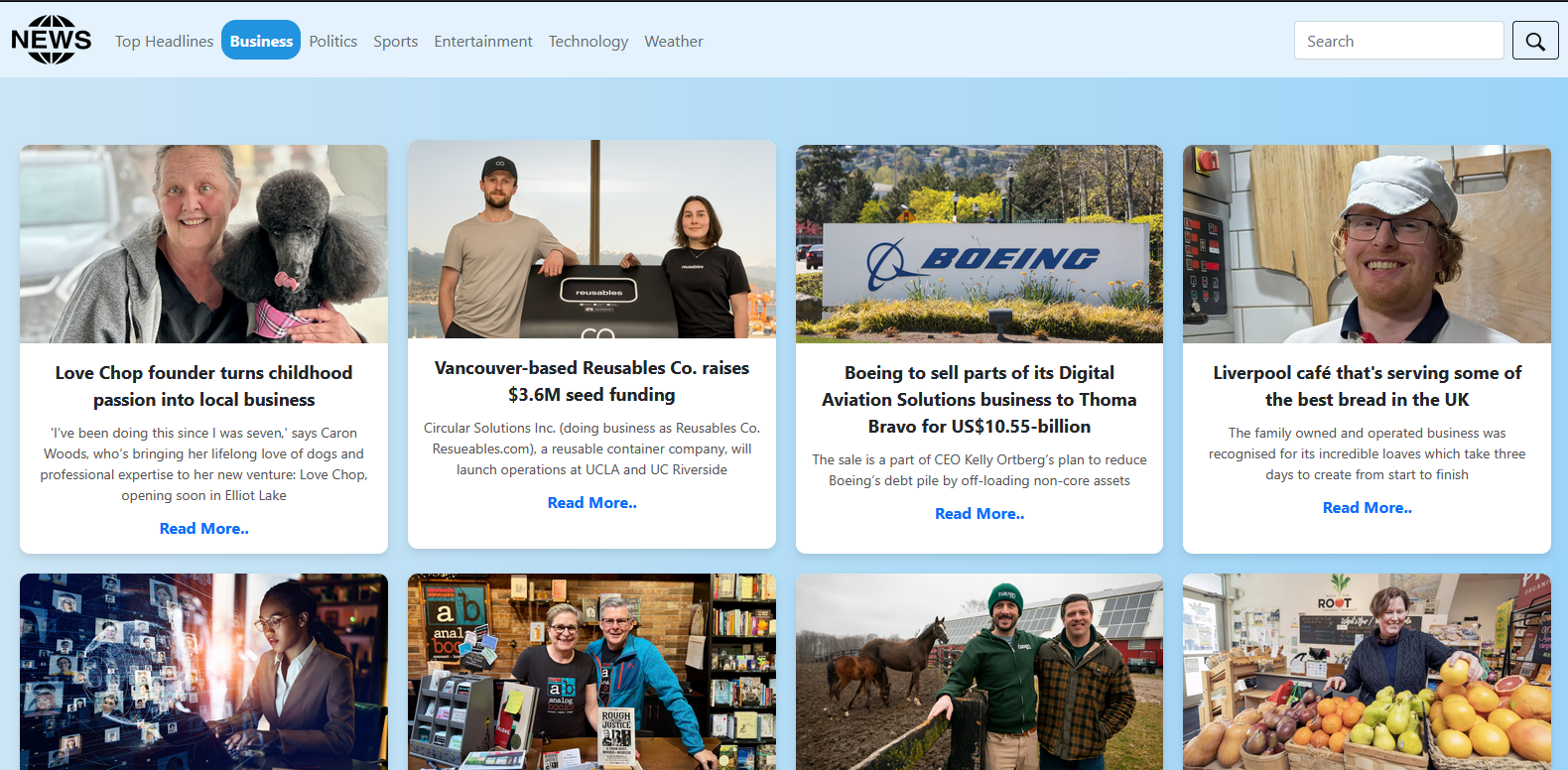
1. News Categories: Users can select from predefined categories like business, sports,
technology, and more.
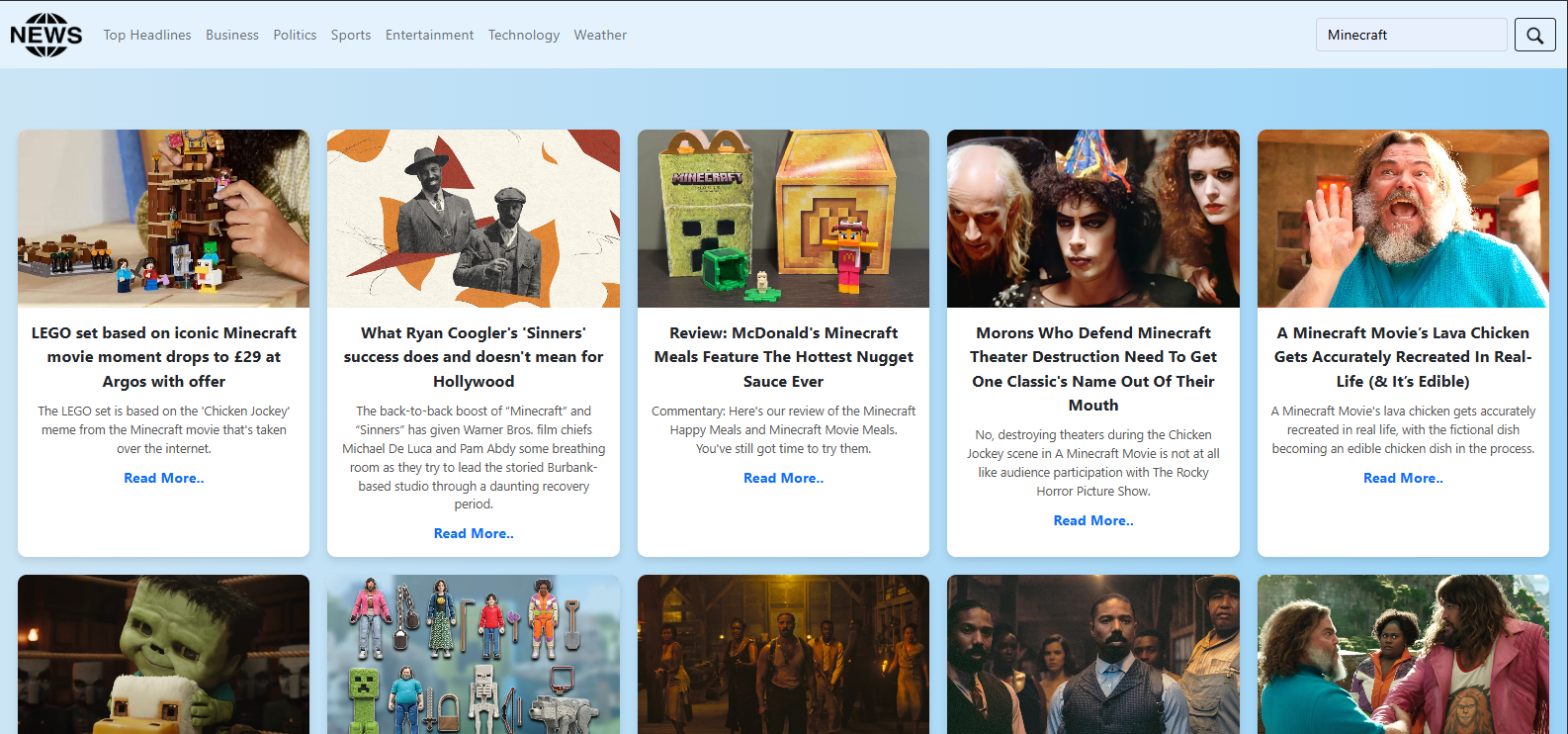
2. Search Bar: A search form allows users to search for specific news topics via a GET
parameter.
3. Dynamic News Display: News content is fetched and displayed dynamically using the fetch()
API without reloading the page.
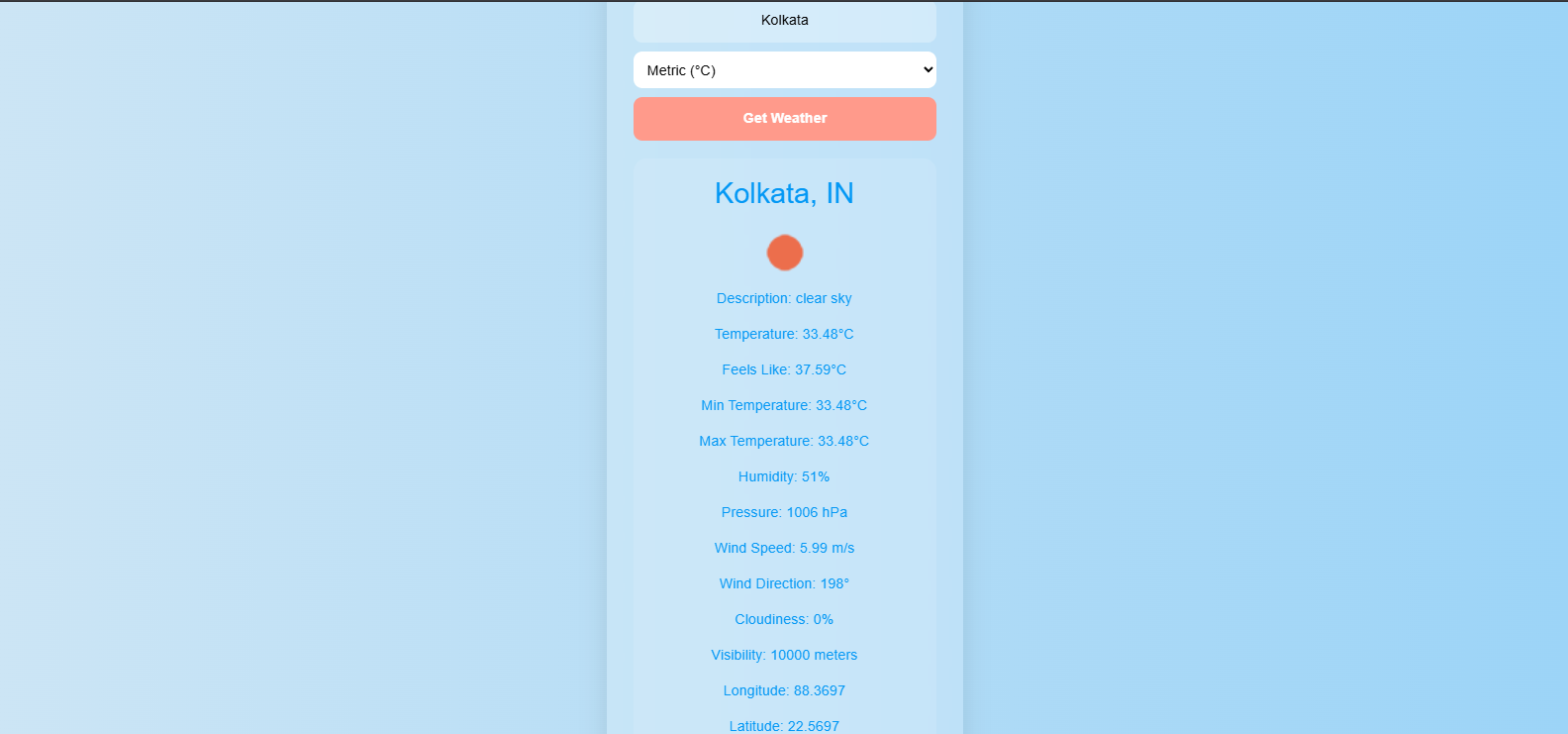
4. Weather Input: Users can enter a city name and select units (metric or imperial) to
fetch current weather data.
5. Weather Data Rendering: Weather information such as temperature, humidity, wind
speed, and cloud coverage is shown using structured HTML elements.
6. Unit Toggle: Temperature display can be switched between °C and °F using a dropdown
menu.
7. Responsive Layout: The interface uses Bootstrap for mobile-friendly and responsive design.
News tabs
Search tab
Weather tab
3. How the Application Internally Works
1. Navigation: The news.html page uses a navbar with category links handled through
data-category attributes.
2. JavaScript Events: Event listeners detect link clicks and trigger fetch() requests to
get_news.php.
3. News Backend: get_news.php receives category or search input, calls a news API, parses the
JSON, and returns relevant results.
4. Weather Page: weather.html contains a form where users enter the city name and unit.
5. Weather Script: weather_script.js sends a POST request to get_weather.php
using fetch(), retrieves JSON data, and updates the weather card elements.
6. Backend Fetch: PHP files use file_get_contents() to call external APIs and return formatted
results to the client.
4. Technical Design Overview
1. Modular HTML: news.html and weather.html are separate pages with a consistent layout
using Bootstrap.
2. Separate Scripts: script.js handles news logic, while weather_script.js manages
weather behavior.
3. Minimal Backend: PHP scripts act as simple middle layers between the front end and external
APIs.
4. Dynamic DOM Updates: The content is rendered directly into the page using JavaScript without page
reloads.
5. Clean API Calls: External APIs are called via fetch() using either GET or
POST requests depending on the use case.